
Reverse
Aging
By Sang Whang
Here
is the simple process of aging.
Every
living cell within our body creates waste products. The
nutrients from our food are delivered to each cell and they
burn with oxygen to provide energy for us to live. The burned
nutrients are the waste products. Whether you eat gourmet
or junk food, all food generates waste products. The food
that is either good or bad for you is determined by the
amount and quality of the wastes produced: toxic, acid,
alkaline, etc. Most of our cells go through metabolism and
old dead cells become waste products. These waste products
must be discharged from our body. In fact, our body tries
its best to dispose of them through urine and perspiration.
Virtually all waste products are acidic; that is why urine
is acidic and skin surface is also acidic.
The problem is that, due to several reasons, our body cannot
get rid of 100% of the waste products it produces.
The
main reason for this is our life style. We stay up late
and get up early. We do not take time to rest; some of us
work more than one job. We, therefore, spend more time producing
waste products than processing and discharging them.
The
second reason is food. Most of the food we like is mainly
acidic. Acidic food does not necessarily mean that it tastes
acidic, but that the wastes it produces are acidic. Grains
and meats are mainly acidic; fruits and vegetables are alkaline.
Citric fruits may taste acidic but they are considered to
be alkaline because they contain alkaline minerals.
The third reason is our environment. More healthy cells
are killed by air, water and soil pollution than the natural
death of cells caused by normal metabolism. Thus, more waste
products are created. The question is: "What happens
to those non-disposed acidic waste products?" The answer
is simple. These waste products become solid wastes, such
as, cholesterol, fatty acid, uric acid, kidney stones, urates,
phosphates, sulfates, etc., and, unknown to us, they accumulate
and build-up somewhere within our body. This accumulation
of non-disposed acidic wastes within our body is the aging
process.
Alkaline neutralizes acid. Drinking alkaline water helps
our body dissolve acid wastes and make it easier for the
body to dispose of them safely. Since the accumulation of
acid wastes is aging, the reduction of acid wastes is reverse
aging. Alkaline water is not a medicine to cure any disease.
However, if consumed regularly, alkaline water gradually
reduces the accumulated acid wastes. As a result of acid
reduction, there are many reports of natural health improvement
in Japan. We use alkaline soap to wash acidic dirt accumulated
on our skin; we must wash the acidic dirt accumulated within
our body by using alkaline water. Alkaline water has been
available in Asia for over 30 years.
Water ionizers to produce alkaline water have been approved
by Japanese government agencies as medical devices.
In future publications more detailed scientific explanations
will be discussed on the subjects of water, acidity and
alkalinity, effects of acidic wastes on the human body,
causes of some adult diseases, effects of alkaline water,
and simple methods of making alkaline water. Find
your true age here. --
From
Yogi Bhajan

"No
matter how good the diet is, we tend to
exceed the self cleaning capacity of our bodies.
Uric acid (a biproduct of
meat consumption),
calcium crystals, and many other wastes and
poisons get stored in tissues and joints. They
make us stiff and may cause many diseases.
In Kundalini Yoga, muscle
stretching and internal
massage bring waste back
into circulation so that the
lungs, intestines, kidneys, and skin are able to remove
it."
Yogi Bhajan


Is
this preservative, Benzoate of Soda,
(Sodium Benzoate) bad for you?
Diet
Coke will drop additive in DNA damage fear.
By Colin Fernandez
May
26th - Diet Coke to drop additive in DNA damage fear. May
be linked to hyperactivity and DNA damage.
Coca-Cola is phasing out a controversial additive that has
been linked to damage to DNA and hyperactivity in children.
Sodium benzoate, also known as E211, is used to stop fizzy
drinks going moldy.
Coca-Cola said it had begun withdrawing the additive from
Diet Coke in January in response to consumer demand for
more natural products.

By the end of the year no can or bottle will contain E211.
The company plans to remove it from its other products as
soon as possible, but said that at present it had not found
a satisfactory alternative to replace the additive in some
soft drinks with a higher juice content, including Fanta,
Dr Pepper, Sprite and Oasis. The chemical is not used in
regular Coke.
While sodium benzoate occurs naturally in some fruits, it
is used in greater strengths by the soft drinks industry.
But research by Peter Piper, a professor of molecular biology
at Sheffield University, found that the additive could switch
off parts of DNA, the genetic code in the cells of living
creatures, that could be linked to cirrhosis of the liver
and Parkinson's disease.
However, the Government-backed Committee on Mutagenicity
has dismissed the research.
It argues that while sodium benzoate has been shown to be
harmful to yeast cells, human cells are stronger.
Research by Southampton University found that sodium benzoate
was one of seven additives - the six others are food colors
- that can lead to hyperactivity in children.
The Food Standards Agency has called for the six colors
to be withdrawn from products but not sodium benzoate.
The Daily Mail has campaigned for a ban on harmful additives.
A Coca-Cola spokesman said: "We are continuously listening
to our consumers' thoughts about ingredients."
The firm stressed that E211 was approved as an additive
by many bodies around the world including the European Food
Standards Agency.

BUTTER
IS BETTER FOR YOUR HEALTH

Do You Know?
The differences between Margarine and Butter.
 Margarine was originally manufactured
to fatten turkeys. Then, they came out with some clever
and different flavorings to improve the taste for public
consumption.
Margarine was originally manufactured
to fatten turkeys. Then, they came out with some clever
and different flavorings to improve the taste for public
consumption.
 Both margarine and butter have
the same amount of calories.
Both margarine and butter have
the same amount of calories.
 Butter is slightly higher in
saturated fats at 8 grams compared to 5 grams.
Butter is slightly higher in
saturated fats at 8 grams compared to 5 grams.
 Eating margarine can increase
heart disease in women by 50% over eating the same amount
of butter, according to a recent Harvard medical study. See
Snopes.com.
Eating margarine can increase
heart disease in women by 50% over eating the same amount
of butter, according to a recent Harvard medical study. See
Snopes.com.
 But eating butter increases
the absorption of many other nutrients in other foods.
But eating butter increases
the absorption of many other nutrients in other foods.
 Butter has many nutritional
benefits, whereas margarine has only a few, but only because
they are added!
Butter has many nutritional
benefits, whereas margarine has only a few, but only because
they are added!
 Butter tastes much better than
margarine, and it can enhance the flavors of other foods.
Butter tastes much better than
margarine, and it can enhance the flavors of other foods.
 Butter has been around for
centuries, whereas margarine has been around for less than
100 years.
Butter has been around for
centuries, whereas margarine has been around for less than
100 years.
MORE ABOUT MARGARINE
 Margarine is very high in trans
fatty acids.
Margarine is very high in trans
fatty acids.
 Margarine triples the risk
of coronary heart disease. See
Snopes.com.
Margarine triples the risk
of coronary heart disease. See
Snopes.com.
 Margarine increases total cholesterol
and LDL, the bad cholesterol, and lowers HDL cholesterol,
the good cholesterol.
Margarine increases total cholesterol
and LDL, the bad cholesterol, and lowers HDL cholesterol,
the good cholesterol.
 Margarine increases the risk
of cancers up to five fold.
Margarine increases the risk
of cancers up to five fold.
 Margarine lowers the quality
of breast milk.
Margarine lowers the quality
of breast milk.
 Margarine decreases the immune
system response.
Margarine decreases the immune
system response.
 Margarine decreases insulin
response.
Margarine decreases insulin
response.
WHAT‘S REALLY DISTURBING

Margarine is only ONE MOLECULE away from being all PLASTIC.
This fact alone is enough to make anybody avoid margarine
for life and anything else that is hydrogenated (this means
hydrogen is added, changing the molecular structure of the
substance).
Try this:
Purchase a tub of margarine and leave it in your garage
or shaded area. Within a couple of days you will note a
couple of things:
No flies, not even those pesky fruit flies will go near
margarine (this should tell us something).
Margarine does not rot or smell differently because it has
no nutritional value; nothing will grow on it. Even those
teeny weenie microorganisms will not a find a home to grow
in margarine. Why, because it is PLASTIC.
Question:
Would you melt some Tupperware and spread it on your toast?
--
The
History of Butter
How
To Make Ghee (Clarified Butter)

Health
facts about Honey and Cinnamon


It's
been found that a mixture of Honey and Cinnamon cures many
diseases. Honey is produced in most of the countries of
the world. Scientists today also accept honey as a very
effective medicine for all kinds of diseases. Honey can
be used without any side effects for any kind of diseases.
Today's scientists say that even though honey is sweet,
if taken in correct dosage as a medicine, it does not harm
diabetic patients.
Weekly World News, a magazine in Canada, on its issue dated
January 17, 1995 has given the following list of diseases
that can be cured by Honey and Cinnamon as researched by
some scientists:
HEART DISEASES:
Make a paste of honey and cinnamon powder, apply on bread,
instead of jelly or jam, and eat it regularly for breakfast.
It reduces the cholesterol in the arteries and saves the
patient from heart attack. Also, those who have previously
had an attack, if done daily, will prevent future heart
attack.
Regular use of this combination relieves shortness of breath
and strengthens heartbeat. In America and Canada, some nursing
homes have treated patients successfully with honey and
cinnamon, having found that it revitalizes the arteries
and veins.
ARTHRITIS:
Arthritis patients may take daily, morning and night, one
cup of hot water with two spoons of honey and one spoon
of cinnamon powder. This can cure even chronic arthritis.
In research conducted at the Copenhagen University, it was
found that when patients were treated with a mixture of
one Tablespoon honey and half a teaspoon of cinnamon powder
before breakfast, out of the 200 people so treated, 73 patients
were relieved of pain within a week, and within a month,
most patients who could not walk or move around because
of arthritis, were walking without pain.
BLADDER INFECTIONS:
Take two Tablespoons of cinnamon powder and one teaspoon
of honey in a glass of lukewarm water and drink it. This
destroys the organisms in the bladder.
TOOTHACHE:
Make a paste of one teaspoon of cinnamon powder and five
teaspoons of honey and apply on the aching tooth. This may
be applied 3 times a day till the tooth stops aching.
CHOLESTEROL:
Two Tablespoons of honey and three teaspoons of cinnamon
powder mixed in 16 ounces of tea water, given to a cholesterol
patient, is found to reduce the level of cholesterol in
the blood by 10% within 2 hours. As mentioned for arthritic
patients, if taken 3 times a day, any chronic cholesterol
is cured. Pure honey taken daily with food relieves elevated
cholesterol.
COLDS:
Those suffering from common cold symptoms should take one
Tablespoon lukewarm honey and water with 1/4 spoon cinnamon
powder daily for 3 days. This process will cure most chronic
cold symptoms, and clear the sinuses.
UPSET STOMACH:
Honey taken with cinnamon powder cures stomach ache and
also clears stomach ulcers.
GAS:
According to studies done in India and Japan, if honey is
taken with cinnamon powder the stomach gas is relieved.
IMMUNE SYSTEM:
Daily use of honey and cinnamon powder strengthens the immune
system and protects the body from bacterial and viral attacks.
Scientists have found that honey has various vitamins and
iron in large amounts. Constant use of honey strengthens
the white blood corpuscles to fight bacterial and viral
diseases.
INDIGESTION:
Cinnamon powder sprinkled on two Tablespoons of honey taken
before food, relieves acidity and helps digest the heaviest
of meals.
INFLUENZA:
A scientist in Spain has found that honey contains a natural
ingredient which kills the influenza germs and prevents
the flu.
LONGEVITY:
Tea made with honey and cinnamon powder, when taken regularly,
arrests the ravages of old age. Take 4 spoons of honey,
1 spoon of cinnamon powder and 3 cups of water and boil
to make like tea. Drink 1/4 cup, 3 to 4 times a day. It
keeps the skin fresh and soft.
PIMPLES:
Three Tablespoons of honey and one teaspoon of cinnamon
powder paste. Apply this paste on the pimples before sleeping
and remove it next morning with warm water. If done daily
for two weeks, it removes the pimples.
SKIN INFECTIONS:
Regular application of honey and cinnamon powder in equal
parts to the affected parts cures eczema, ringworm, and
all types of skin infections.
WEIGHT LOSS:
Daily in the morning 1/2 hour before breakfast on an empty
stomach and at night before sleeping, drink honey and cinnamon
powder boiled in one-cup water. If taken regularly it curbs
the appetite and reduces the weight of even the most obese
person. Also, the frequent drinking of this mixture does
not allow fat to accumulate in the body even though the
person may eat a high calorie diet.
CANCER:
Recent research in Japan and Australia has revealed that
advanced cancer of the stomach and bones have been cured
successfully. Patients suffering from these kinds of cancer
should take one Tablespoon of honey with one teaspoon of
cinnamon powder daily 3 times a day for 40 days.
FATIGUE:
Recent studies have shown that the sugar content of honey
is more helpful rather than being detrimental to the strength
of the body. Senior citizens, who take honey and cinnamon
powder in equal parts, are more alert and flexible. One
researcher says that half a Tablespoon of honey in a glass
of water and sprinkled with cinnamon powder, taken twice
daily, increases the vitality of the body within a week.
--

The
Miracle of Hydrogen Peroxide

These
are the benefits of that plain little ole bottle of 3% hydrogen
peroxide you can get for under $1.00 at any drug store.
Most
doctors don't tell you about hydrogen peroxide. Have you
ever smelled bleach in a doctor's office? Why? Because it
smells, it's toxic, it is not healthy! Ask the nurses who
work in the doctor's offices about it.
Did you also know bleach was invented in the late 40's?
It's chlorine! And it was used to kill many people.
Peroxide
was invented during WWI in the 20's. It was used to save
lives and helped to cleanse wounds and hospital areas.
Try
these:
 Take one capful (the little
white cap that comes with the bottle) and hold in your mouth
for 10 minutes daily, then expel it. (Do it when you bathe.)
No more canker sores, and your teeth will be whiter without
expensive pastes. Use it instead of mouthwash.
Take one capful (the little
white cap that comes with the bottle) and hold in your mouth
for 10 minutes daily, then expel it. (Do it when you bathe.)
No more canker sores, and your teeth will be whiter without
expensive pastes. Use it instead of mouthwash.
 Let toothbrushes soak in a
cup of peroxide to keep them free of germs.
Let toothbrushes soak in a
cup of peroxide to keep them free of germs.
 Clean counters and table tops
with peroxide to kill germs and leave a fresh smell. Simply
put a little on your dishrag when you wipe, or spray it
on the counters.
Clean counters and table tops
with peroxide to kill germs and leave a fresh smell. Simply
put a little on your dishrag when you wipe, or spray it
on the counters.
 Pour peroxide on your wooden
cutting board after rinsing it off to kill salmonella and
other bacteria.
Pour peroxide on your wooden
cutting board after rinsing it off to kill salmonella and
other bacteria.
 Spray a 50/50 mixture of peroxide
and water on any foot fungus (especially the toes) every
night and let dry.
Spray a 50/50 mixture of peroxide
and water on any foot fungus (especially the toes) every
night and let dry.
 Soak any infections or cuts
in 3% peroxide for five to ten minutes several times a day.
Combat troops have seen gangrene that would not heal with
any medicine, but was healed by soaking in peroxide.
Soak any infections or cuts
in 3% peroxide for five to ten minutes several times a day.
Combat troops have seen gangrene that would not heal with
any medicine, but was healed by soaking in peroxide.
 Fill a spray bottle with a
50/50 mixture of peroxide and water and keep it in every
bathroom to disinfect without harming your septic system
like bleach and many other disinfectants will.
Fill a spray bottle with a
50/50 mixture of peroxide and water and keep it in every
bathroom to disinfect without harming your septic system
like bleach and many other disinfectants will.
 Tilt your head back and spray
this 50/50 mixture into your nostrils whenever you have
a cold or plugged sinuses. It will bubble and help to kill
the bacteria. Hold for a few minutes, and then blow your
nose into a tissue.
Tilt your head back and spray
this 50/50 mixture into your nostrils whenever you have
a cold or plugged sinuses. It will bubble and help to kill
the bacteria. Hold for a few minutes, and then blow your
nose into a tissue.
 If you cannot get to a dentist
right away with a toothache, put a capful of 3% peroxide
into your mouth and hold it for ten minutes several times
a day. The pain will lessen greatly.
If you cannot get to a dentist
right away with a toothache, put a capful of 3% peroxide
into your mouth and hold it for ten minutes several times
a day. The pain will lessen greatly.
 Spray the 50/50 solution on
your wet hair after a shower and comb it through. You will
not have the peroxide-burnt blonde hair like the hair dye
packages but more natural highlights if your hair is a light
brown, faddish, or dirty blonde. It also lightens gradually,
so it's not a drastic change.
Spray the 50/50 solution on
your wet hair after a shower and comb it through. You will
not have the peroxide-burnt blonde hair like the hair dye
packages but more natural highlights if your hair is a light
brown, faddish, or dirty blonde. It also lightens gradually,
so it's not a drastic change.
 Put half a bottle of peroxide
in your bath to help rid boils, fungus, or other skin infections.
Put half a bottle of peroxide
in your bath to help rid boils, fungus, or other skin infections.
 Add a cup of peroxide instead
of bleach to a load of whites in your laundry to whiten
them. If there is blood on clothing, pour it directly on
the soiled spot. Let it sit for a minute, then rub it and
rinse with cold water. Repeat if necessary.
Add a cup of peroxide instead
of bleach to a load of whites in your laundry to whiten
them. If there is blood on clothing, pour it directly on
the soiled spot. Let it sit for a minute, then rub it and
rinse with cold water. Repeat if necessary.
 Use peroxide to clean mirrors.
There is no smearing. --
Use peroxide to clean mirrors.
There is no smearing. --

Operating
Blind
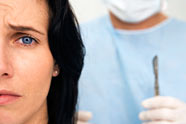
Courtesy
of Prevention Magazine
Every
year, nearly 2.5 million people go under the knife unnecessarily,
often with devastating consequences. Make sure you're not
one of them.
Two years ago, when Leah Coppersmith went in for back surgery,
she expected to be lacing up her running shoes within days.
She's been in pain ever since.
A car accident in 1991 left this mother of four with nagging
lower-back pain -- annoying, but not bad enough to keep
her from running 5-Ks. But in 2005, the nag grew to a scream.
An MRI revealed that two disks -- the gel-filled cushions
between the vertebrae -- were badly worn. Coppersmith expected
the doctor to recommend a diskectomy, in which part of a
troublesome disk is removed to relieve pressure on the nerve;
the low-risk surgery had helped her once before. But this
time, the surgeon wanted to replace a disk with an artificial
one. The procedure was getting great results, he said. Coppersmith
was skeptical until he told her she'd be back running 5-Ks
again in no time. She laughs bitterly at the memory.
Pain is now the defining feature of her life. She can't
sit down to family dinners. She quit her job because she
can't work at a desk. Her misery has company: While looking
for help online, she found a study showing that 64% of people
who received the disk, called the Charité, still
needed narcotic painkillers 2 years after surgery.
Every year, upward of 15 million Americans go under the
knife -- and for most of them, surgery provides relief or
a new lease on life. Joints are replaced, organs are transplanted,
lives are saved. But Congress has estimated that surgeons
perform 2.4 million unnecessary surgeries a year in the
United States, with a cost of roughly $3.9 billion -- and
a toll of about 11,900 deaths. The reason isn't simple.
"The majority of surgeons who perform these procedures
are actually very enthusiastic about their benefits,"
says Mark Chassin, MD, chair of the department of health
policy at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. "It's not
like they get up in the morning and ask themselves, How
many unnecessary procedures can I do today? But there's
a lot of financial incentive to do surgery that may not
benefit the patient, and very little oversight."
So how do you know when someone is suggesting surgery you
don't need -- and what can you do to prevent it? Your first
line of defense is to become your own advocate. One study
showed that when patients and doctors share the decision
making, rates of surgery drop by as much as 44%. Here, we
explain what's behind four of the procedures most often
done unnecessarily and give you expert advice on the best
alternatives.
BE SKEPTICAL: SPINAL SURGERY
The waiting room of Charles Rosen, MD, a spinal surgeon
and an associate professor of orthopedic surgery at the
University of California, Irvine, was filled with patients
who, like Coppersmith, had failed disk implants. "In
my 20 years of orthopedics, I'd never seen so many people
in such a severe state of constant pain," he says.
So Rosen examined the evidence backing the Charité
disk. He was shocked to see that the researchers had compared
patients who got the disk with those who received a type
of fusion surgery with a particularly high failure rate
-- 60%. (Even before the study's publication, that procedure
had been largely abandoned.) Then he discovered that researchers
on other Chariti studies were paid consultants for the device
maker. Outraged, Rosen founded the Association of Ethical
Spine Surgeons. Members agree not to take money from device
makers or form partnerships with the companies.
The spine is ground zero for unnecessary surgeries partly
because back pain is incredibly common and notoriously tough
to treat. More than 1 million sufferers opt for surgery
each year, and spinal fusion -- the use of bone grafts,
screws, and other devices to secure one or more vertebrae
-- is one of the most popular choices. Between 1996 and
2001, the number of spinal fusions skyrocketed 113%, while
the number of knee- and hip-replacement surgeries rose just
15% and 13%, respectively. But unlike those procedures,
spinal surgeries often fail -- instead of relieving pain,
they can turn it into agony. According to Aaron Filler,
MD, PhD, director of the Peripheral Nerve Surgery Program,
Institute for Spinal Disorders, at Cedars-Sinai Medical
Center in Los Angeles, there are tremendous rewards for
spinal surgeons who do aggressive procedures: Because of
the hardware involved, an operation on the spine can pay
a surgeon 10 times as much as one on the brain. Yet the
moneymaking back surgeries help in only a small proportion
of cases. What's more, back surgeons are rarely held accountable
if the operation fails. "The referring doctor has low
expectations," Filler says. "So does the patient,
because everyone thinks of back problems as so difficult
to treat."
Protect Yourself
Pinpoint the pain: If your doctor labels your back pain
as "nonspecific," it means he doesn't know the
cause; if he suggests surgery, alarm bells should go off,
says Filler. Spinal fusion is most beneficial when vertebrae
slip out of place and press on the ones below, which is
easily detected on an x-ray. "When properly done for
the right reasons, spinal surgery can be extremely effective,"
says Filler.
Make lifestyle adjustments: A 2003 study compared spinal
fusion surgery with a lifestyle approach to back pain: Docs
taught patients how to protect their backs, by bending at
the knees when lifting, for instance. They also encouraged
exercise, like water aerobics. A year later, the nonsurgical
approach reduced pain and increased mobility just as much
as surgery did. Alternative treatments such as chiropractic
and acupuncture can also pay off, studies show. For more
info on finding alternative treatments, go to prevention.com/links.
Consider a helpful shot: A nerve-blocking injection called
an epidural, given by a surgeon or a rehab specialist like
a physiatrist, may quiet the pain for up to a year; it helps
in about 50% of patients.
Skip the hardware: If surgery seems like the right approach,
get the simplest procedure possible. There's a much smaller
chance of complications if you have a diskectomy, for example,
than if you have an artificial disk implanted.
BE SKEPTICAL: HYSTERECTOMY
Lori Jo Vest was 36 when three doctors told her a hysterectomy
was the only fix for her heavy bleeding caused by uterine
fibroids. Terrified that she'd be thrust into early menopause
-- in half of all hysterectomies, surgeons end up removing
the ovaries, too -- Vest went online and discovered myomectomy,
in which the surgeon cuts out the fibroids, sparing the
uterus. But her doctors nixed the idea; after all, they
said, Vest, who had a toddler, didn't want more children.
Then Vest called the nearby University of Michigan, Ann
Arbor -- and nearly leaped through the phone when she heard
they had a clinic for women seeking alternatives to hysterectomy.
"The doctor said I was a perfect candidate for myomectomy,"
Vest says. She also told Vest that many surgeons dislike
the surgery because it's more difficult than a hysterectomy.
Now 44, Vest no longer is troubled by heavy bleeding, but
she still has her uterus and ovaries. *"I don't want
to go through menopause until my body is ready," she
says.
Hysterectomy is second only to C-section as the most common
surgery performed on women in the United States. Each year
more than 600,000 Americans have the procedure -- twice
the rate as in England. A 2000 study found that 70% of the
hysterectomies performed in nine Southern California managed-care
organizations were recommended inappropriately. "The
most common mistake we saw was that doctors didn't try safer,
less-invasive approaches first," says lead author Michael
Broder, MD, an assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology
at UCLA's David Geffen School of Medicine.
Hysterectomy can be warranted if a woman has cancer, and
it can be the right choice in other cases, too -- for instance,
if medical treatment didn't get your bleeding under adequate
control, and you don't want to try a surgery like myomectomy
because of the risk of recurrence. But unless you have cancer,
"having a doctor say, 'You absolutely need a hysterectomy,'
is akin to a waiter at a restaurant saying, 'You've got
to have the steak,'" says Malcolm G. Munro, MD, a professor
of obstetrics and gynecology at UCLA. "A good doctor
should give you a menu of choices."
Protect Yourself
Try hormones or drugs first: Most hysterectomies are done
on women under age 45, but if you can manage symptoms of
fibroids with medication until menopause, symptoms usually
ease naturally. Birth control pills or other drugs help
control irregular bleeding. Also check into getting a progestin-releasing
IUD (Mirena): It can dramatically decrease bleeding caused
by fibroids.
Consider a less drastic procedure: Like myomectomy, uterine
fibroid embolization (UFE) preserves the uterus: An "interventional"
radiologist carefully closes off blood vessels feeding the
fibroids, starving them. A woman may need more treatment
after either procedure if the fibroids come back, and both
cause a fair amount of discomfort. (UFE can require serious
pain meds, although recovery is quicker than after a hysterectomy,
and the risks are lower.) For more info on hysterectomy
alternatives, go to prevention.com/links.
BE SKEPTICAL: ANGIOPLASTY
When Irwin Melnicoff, a forensic engineer in Boynton Beach,
FL, felt a stabbing chest pain at age 45, he went straight
to the cardiologist. The diagnosis? A narrowed artery. The
answer? Angioplasty. But Melnicoff was scared of surgery;
even when the doctor told him he'd die without the artery-opening
procedure, he chose drug therapy instead. (He also chose
a new doctor.) That was 25 years ago. With the help of daily
heart medications, his chest pain vanished. He walks 30
minutes a day, 7 days a week, and feels great.
He made the right choice. Though angioplasty has been hailed
by some as a wonder fix for decades, it now turns out that
most of the time, the procedure doesn't help. Angioplasty
can save your life if it's done during or right after a
heart attack. But in other circumstances, it may not do
you much good.
"Doctors used to think of heart disease as a plumbing
problem -- that arteries were like drainpipes gradually
being clogged by plaque made up mostly of cholesterol,"
says Arthur Agatston, MD, a preventive cardiologist and
author of The South Beach Heart Program. So it seemed to
make sense to use angioplasty, in which a small balloon
is inflated in the artery, to get that gunk out of the way
by squashing it against the vessel wall. However, research
has since shown that problematic plaque actually forms within
the delicate inner lining of artery walls.
What does cause a heart attack? If the plaque within the
wall ruptures, it injures the artery, producing a blood
clot as part of the healing process. Unfortunately, the
clot can close off the entire artery -- that's a heart attack,
and you need angioplasty or bypass surgery immediately.
If you have angioplasty, the doctor may also insert a stent,
a mesh scaffolding, to hold open the artery.
But if you're not having a heart attack, angioplasty (with
or without a stent) won't help and may even do some harm.
That's the news from a large trial published in April in
the New England Journal of Medicine. People with "stable"
heart disease -- they weren't having a heart attack, but
a vessel was at least 70% closed -- fared no worse if they
received medical therapy, such as aspirin, blood thinners,
and cholesterol-lowering drugs, than if they got angioplasty.
During the next 4 1/2 years, neither group was more likely
to have a heart attack or stroke or die.
A study published late last year helps pinpoint exactly
when it's worth getting angioplasty. That trial showed that
if the procedure was done 3 or more days after a heart attack,
it didn't help. "We were very surprised -- we thought
angioplasty would be beneficial even if it was done later,"
says lead author Judith Hochman, MD, director of the cardiovascular
clinical research center at New York University School of
Medicine. "But that's why we do studies: to see if
the patient really does benefit."
Protect Yourself
Insist on being convinced: If your doctor says you need
a non-emergency angioplasty, ask if it will prolong your
life. "That question puts a cardiologist on the spot,"
says Agatston. If the procedure isn't needed to save your
life, it still may make sense if angina (bouts of chest
discomfort caused by a lack of blood flow to the heart)
interferes with daily activities. But get a second opinion
-- from a preventive cardiologist, not a cardiac surgeon.
Eat right, exercise, and lose weight if necessary: You needn't
avoid fats and carbs to keep your heart healthy -- just
choose wisely. A diet high in omega-3-rich canola and olive
oils can actually protect your heart. High-fiber carbs in
whole grains, fruits, and veggies also help get fats out
of your blood.
Use the meds known to save lives: Many people with high
cholesterol aren't on statins, though the drugs slash the
risk of heart attack by more than 30%. Similarly, most people
with high blood pressure don't get adequate treatment, studies
show. Lifestyle changes can bring down both cholesterol
and BP, but if they're not enough, medication can be lifesaving.
Your doctor may also put you on daily aspirin or another
drug to lower the risk of a blood clot.
BE SKEPTICAL: KNEE ARTHROSCOPY
Soon after Diana Aceti turned 50, the ache in her knee began
to keep her from walking and playing tennis, two activities
she loved. An orthopedist said that she had a small tear
in her cartilage and recommended arthroscopic surgery. "He
said I'd back on my feet in a few weeks," says the
public relations director from Bridgehampton, NY.
But afterward, Aceti's knee hurt worse than ever. So she
got a second opinion -- and the news wasn't good. In a rare
complication, her cartilage was damaged beyond repair, and
she needed a partial knee replacement. "Doctors talk
about surgery like it's getting your teeth cleaned,"
says Aceti. "If he'd told me this was a possibility,
I never would have done it."
Knee arthroscopy is most often used for people, like Aceti,
who have osteoarthritis -- cartilage damaged by wear and
tear. A surgeon makes small incisions and inserts instruments
to remove tissue fragments and wash out the joint in the
hopes of reducing pain. Yet in 2002, when knee arthroscopy
was put to the test in a randomized, controlled trial, it
failed royally. Osteoarthritis patients given arthroscopy
reported no more improvement than those who got sham surgery
-- incisions were made but no arthroscope was inserted.
Still, 5 years later, the procedure remains among the top
10 outpatient surgeries: More than 650,000 knee arthroscopies
are performed annually.
Critics say that almost everyone has small tears in their
knee cartilage visible on MRI's, providing a never-fail
excuse for surgery. "Patients have arthroscopy for
what is clearly the result of a bruise or a bump,"
says Ronald Grelsamer, MD, an associate professor of orthopedic
surgery at Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York City.
"For many orthopedists it's the only way left to make
a half-decent living. Does that justify it? No."
The procedure can help in certain situations, Grelsamer
says: If a piece of cartilage is catching, like a hangnail,
clipping it can make you feel better. And some doctors still
believe that for some osteoarthritis patients, flushing
the interior of the knee during arthroscopy can ease pain,
perhaps by getting rid of irritating chemicals. Researchers
can't predict who will benefit from a washout, though --
and surgeon Bruce J. Moseley, MD, who led the sham surgery
comparison, argues that any improvement in arthritis patients
is due to the placebo effect.
Protect Yourself
Wait a while: Arthroscopy is most frequently done after
a twist or fall, but those injuries often get better within
a few months with physical therapy, anti-inflammatory meds,
a cortisone injection -- or just the passage of time.
Be skeptical of MRI results: Arthroscopy is most apt to
help if there's a detached fragment of cartilage or a severe
tear -- a 3 on a 1-to-3 scale, as rated by a radiologist.
But even a bad tear may not cause pain, so ask whether it
matches up with the area that hurts. --



About
Hair
Eyes
Have It
Tell The FDA
Ear
Candling
Back
Walking
Energy-Drinks
The
Water Cure
Inner
Clean Diet
What
About Gout
For
Women Only
The
Human Body
For
Garlic Lovers
Reflexology
Chart
Path2Fitness.com
What's
Eating You
Yogi
Bhajan's Diet
Vegetarian
Recipes
A
Healing Meditation
Food
Ads vs. Reality
Drunk...Driving...Dead
Test
Your Eyes Online
Beware:
Canned Soup
What
About Aspartame
What
About Chemtrails
What
About Gallstones
Meditation
For Women
How
To Reverse Aging
The
Color of Depression
Beware:
"No Added MSG"
Do
Doctors Cause Dementia
What
About Sodium Benzoate
It's
Time To Rag On Ragweed
SugarIsAFourLetterWord.com
Left
Brain-Right Brain Diversity
Be
Warned If You're On Statins
10
Warning Signs of Alzheimer's
Drug
company insider confesses
Lasik
Eye Surgery - FDA Warning
Corporations
are killing Americans
A
Critical Look At Optical Retailers
Jimmy
Carter And Women's Rights
What
Your Optician Needs To Know
Is
Alzheimer's Diabetes of The Brain
Appendix:
A Newly Discovered Organ
Another
Side of The Soy-Protein Story
Are
Prescribed Drugs Making You Sick
See
What Happens When You Meditate
See
Why Sikhs Keep Their Hair Unshorn
What
About PPA (PhenylPropanolAmine)
Use
Himalayan Salt - Do Not Use Table Salt
Opticians:
Merchants or Health Care Providers